Chronic prostatitis is a long-term inflammation of the prostate, and the symptoms are usually not present, which is why most male populations do not know about the disease.

The development of chronic prostatitis is the result of an acute process, although this is actually rare.Usually, inflammatory chronic prostatitis begins gradually without any unpleasant symptoms and sensations, and the process of the disease is often discovered by chance during ultrasound examinations.
Young and middle-aged and older people are subject to chronic forms.Prostatitis also threatens those who live an inactive lifestyle through active families, feel excessive physical exercise, and observe sexual quit drinking.
Classification
According to the modern classification of prostatitis developed in 1995, several categories of the disease are distinguished:
- Acute bacterial prostatitis (OBP) is the most common type of prostatitis.It is usually caused by a bacterial infection and is easily diagnosed due to typical signs.Acute bacterial prostatitis may occur at any age.Symptoms include pain in urination, pain in the bladder, lower abdomen, back, or pelvic area.Fever may be accompanied by chills.
- Chronic bacteria Prostatitis is a disease with typical chronic inflammatory symptoms, an increase in the amount of bacteria and white blood cells in the urine, and after its massage is the secret of the prostate.
- Chronic prostatitis (CP) is the most common form of prostatitis.In most cases, this is the result of acute bacterial prostatitis (untreated or poorly treated).If there are symptoms, they occur in the form of pain in the genital or pelvic area, difficulty in urination or painful urination and ejaculation.
- Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis - Using this form of disease, the classic symptoms of prostatitis do not exist and when connected to the clinic for different reasons, the disease itself is discovered by chance.
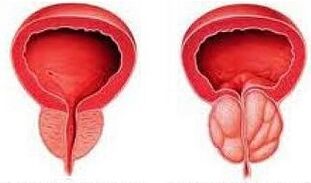
In the presence of infectious components, they indicate bacterial (infectious) chronic prostatitis.In the absence of microbial pathogens - About non-bacterial (non-infectious) prostatitis.It is believed that in 90-95% of the cases, nonbacterial chronic prostatitis occurs, only in 10-5% of the bacteria.
Cause
The occurrence of chronic prostatitis can lead to many factors.First, this is:
- IPP: Chlamydia, urea hyperpolytic bacteria, mycoplasma, herpesvirus, cytomegalovirus, caterpillaria, caterpillaria, caterpillar, acidococcus, primitive ADO, Escherichia coli, Escherichia coli may affect urea and detect PROSTA in tissues;
- Violation of blood circulation in the pelvic organs (stagnation of the prostate causes its inflammation);
- Sitty lifestyle (drivers, office staff, officials);
- Artificial prolonged interruption of sexual desire for sexual intercourse or sexual intercourse is interrupted;
- Regular hypothermia (extremely relaxed enthusiasts: diving, surfing and skiing);
- Stress: mental and physical overload.
The presence and activity of microbial pathogens is not important for the development of chronic prostatitis, because of the status of their pelvic and blood circulation, accompanied by the presence of the disease and the level of protection mechanisms.
Symptoms of chronic prostatitis
Most of the time, as the chronic form of prostatitis develops, the symptoms do not actually disturb men.In this case, all signs of acute prostatitis will not show or be less serious.
The most common symptoms of chronic prostatitis in men are:
- periodic pain and unpleasant sensations in the perineum;
- unpleasant sensations in defecation and urination;
- irradiation of the anus, thighs, testicles;
- releasing from the urethra.
The changes in the course of the disease are no longer very bright and may be so insignificant that patients with chronic prostatitis will not pay much attention to them.
Aggravation of chronic prostatitis
Usually, the aggravation of the disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Pain and burning in the urethra;
- Frequent rushing towards the urine process;
- Pain in the lower abdomen, perineum, and rectum;
- Signs of decreased sexual activity in men;
- Pain during bowel movement.

According to some doctors, it can also distinguish the psychological symptoms of chronic prostatitis, including increased irritability, anxiety, fatigue, temper, sleep disorders, obsession and depression.
It is almost impossible to determine all symptoms of a patient at once, because a person usually shows only 2-3 signs of illness.For example, the most common are impaired erection and pain in the lower abdomen.
Why does prostatitis cause infertility?
The fact is that the prostate creates a special secret that ensures sperm viability.With inflammation, the secretory function of the prostate worsens, which inevitably affects the quality of sperm.
In addition, the prostate is actively involved in the regulation of testosterone production and erectile processes.This is why chronic prostatitis can lead to a decrease in erectile function until it is positive.However, the development of these diseases can be avoided through timely and capable treatment.
Diagnosis
The following procedures are required to help establish/refute the diagnosis:
- Rectangular studies;
- Microscopy of the secrets of the prostate;
- Sow the secrets of the prostate to sensitive antibiotics;
- Sexually transmitted diseases;
- Transorectal ultrasound.
Endoscopy and urodynamic studies are sometimes performed.
How to treat chronic prostatitis
If a person has chronic prostatitis, treatment is always long and difficult.Its duration depends directly on the disease stage where the patient turns to the specialist.Therapy involves a comprehensive approach, i.e. a combination of several methods at the same time:
- antibacterial therapy;
- prostate massage;
- physical therapy procedures;
- correction of diet and lifestyle;
- use of folk therapy;
- surgical treatment.
In addition, anti-inflammatory drugs and anti-neoplastic agents are used to treat the chronic form of the disease.
Medicine treatment
The choice of medication depends on the cause and symptoms of the disease.In order to cure chronic prostatitis of infectious causes, antibacterial drugs:
- fluoroquinolones;
- macrolides;
- tetracyclines were used.

To eliminate inflammation and pain syndrome, pain medications and non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs are used.
Equally in recent years, the treatment of chronic prostatitis is being carried out using drugs that were not previously used for this purpose: alpha-1 blockers, 5-red inhibitors, cytokine inhibitors, immunosuppressants, drugs that affect urea and citrate exchange.
Physical Therapy
Certain physical therapy procedures, such as laser therapy, electrophoresis, transrectal microwave high temperatures, ultrasound speech particles, etc., also help improve the nutritional tissue of the prostate and accelerate the solidification of the tissue.
In addition, prescriptions can be prescribed for chronic prostatitis, healing warm baths, chaos, special enemas.
Prostate massage
It improves the drainage of prostate secrets and microcirculation at the organ level, which in turn helps to recover patients quickly.
Prostate massage cannot be performed with acute prostatitis, hemorrhoids, or rectal fissures.Prostate massage is usually used in combination with antibiotic therapy.A large number of clinical studies have shown that this treatment is highly effective.
Surgery
Surgery can be surgically intervened to remove bacteria-affected prostate areas.Urethral resection is a procedure performed under epidural or intravenous anesthesia.The postoperative recovery period shall not exceed one week.
The methods involved in the treatment of chronic prostatitis are determined by a urologist based on diagnostic information and his actual experience.According to comments on the internet, independent treatment at home is full of consequences.